Imagine your production line grinding to a halt because a single connection failed, spraying fluid everywhere and creating a massive safety hazard. A compromised seal doesn’t just lose oil; it hemorrhages money through downtime and damaged equipment. The solution lies in selecting the precise hydraulic fitting —whether JIC, DIN, or O-Ring—to ensure a leak-free, high-pressure seal that keeps your machinery running without interruption.
What Is a Hydraulic Fitting and How Does It Work?
A hydraulic fitting is a precision-engineered component designed to connect hoses, pipes, and tubes in a hydraulic system, ensuring a sealed pathway for fluid under pressure. These fittings work by creating a mechanical seal—either through threads, O-rings, or metal-to-metal contact—that contains high-pressure hydraulic fluid while allowing for safe flow direction and control.
How do these fittings connect fluid systems?
You might be wondering how a small metal piece holds back thousands of PSI. These components bridge the gap between flexible hoses and rigid machine ports, creating a continuous, sealed circuit.
- They adapt different thread standards.
- They allow for hose rotation and movement.
- They provide secure points for system maintenance.
What are the main components of a fitting?
The anatomy of a fitting determines its pressure rating and application suitability.
- The Body: The main structure housing the fluid passage.
- The Nut: Provides the clamping force.
- The Seat/Seal: The critical interface that prevents leaks.
Why is the seal integrity so critical?
Here’s the deal: system failure is almost always a result of seal compromise. A robust seal prevents fluid bypass, maintains system pressure, and protects against environmental contamination.
Key Takeaway
Proper understanding of fitting mechanics prevents costly system failures.
| Component | Function | Critical Factor | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body | Fluid containment | Material Strength | |
| Nut | Clamping force | Torque Spec | |
| Seat | Leak prevention | Surface Finish |
Analysis: Understanding the three main components allows for faster troubleshooting during maintenance cycles.
Why Use a Stainless Steel Hydraulic Fitting?

Stainless steel hydraulic fittings are the gold standard for environments where failure is not an option due to their exceptional durability and resistance to harsh elements. When your operation requires components that can withstand aggressive washdowns or saltwater exposure, exploring custom stainless steel solutions is essential for long-term reliability.
Is it resistant to rust and chemical corrosion?
You bet it is. The chromium content in stainless steel creates a passive layer that self-heals, making it impervious to rust and many caustic chemicals.
- Resists saltwater corrosion effectively.
- Withstands acidic industrial cleaners.
- Prevents oxidation in humid environments.
Can it handle extreme temperature changes?
Stainless steel maintains its structural integrity across a massive thermal range.
- Remains ductile in cryogenic freezing.
- Retains strength in furnace-adjacent heat.
- Resists thermal shock from rapid cycling.
Which industries require sanitary fittings?
It turns out that industries with strict hygiene mandates rely almost exclusively on this material.
- Food and Beverage processing.
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Marine and Offshore drilling.
Key Takeaway
Stainless steel offers unbeatable longevity in hostile environments.
| Feature | Benefit | Typical Use | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corrosion Resistance | Longer lifespan | Marine/Chemical | |
| Thermal Stability | Safety in extremes | Foundries/Cryogenics | |
| Sanitary Surface | Easy cleaning | Food/Pharma |
Analysis: While the initial cost is higher, the reduced replacement frequency makes stainless steel the most economical choice over time.
When Is a Brass Hydraulic Fitting the Best Option?

Brass hydraulic fittings are often the best option for low-to-medium pressure systems where corrosion resistance and ease of machining are prioritized over extreme tensile strength. They offer excellent conductivity and durability without the high cost of stainless steel, making them a staple in general industrial applications.
Is brass suitable for low-pressure systems?
Here is the truth: Brass is perfect for systems that don’t experience massive pressure spikes.
- Ideal for cooling water lines.
- Perfect for pneumatic control systems.
- Safe for low-pressure fuel transfer.
How does brass resist corrosion?
Brass naturally fights off tarnish and rust in non-acidic environments.
- Excellent against water and air oxidation.
- Resistant to many petroleum products.
- Long-lasting in standard atmospheric conditions.
Why is it popular for automotive tasks?
You usually find brass in the automotive world because it is soft enough to create a tight seal without damaging harder ports.
- Used in brake line junctions.
- Common in coolant sensors and valves.
- Standard for fuel line connectors.
Key Takeaway
Brass balances performance and cost for low-pressure applications.
| Attribute | Rating | Best Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Handling | Low/Medium | Pneumatics/Coolant | |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Water/Air | |
| Cost Efficiency | High | Automotive/General |
Analysis: Select brass for non-critical, lower pressure lines to save costs without sacrificing basic durability.
How Does an O-Ring Face Seal Hydraulic Fitting Stop Leaks?

An O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) hydraulic fitting stops leaks by compressing a resilient elastomeric seal between two flat metal surfaces, creating a virtually impenetrable barrier against fluid migration. This design eliminates the reliance on metal deformation for sealing, which is a common failure point in traditional tapered thread fittings.
Can ORFS fittings handle 6000+ PSI?
Surprisingly, yes. The design actually seals tighter as system pressure increases, pushing the O-ring against the metal wall.
- Rated for high-pressure hydraulic circuits.
- Maintains integrity under pressure spikes.
- Prevents “weeping” common in NPT fittings.
Why are they ideal for vibration control?
What’s the real story? The elastomeric ring absorbs shock and vibration that would crack a metal-to-metal seal.
- Dampens pump harmonics.
- Resists loosening from machinery chatter.
- Protects the threading from fatigue.
Are these seals reusable?
Unlike tapered fittings that deform permanently, ORFS connections can be reassembled.
- Flat faces prevent component wear.
- Only the O-ring typically needs replacement.
- Ideal for maintenance-heavy systems.
Key Takeaway
ORFS is the superior choice for high-pressure, high-vibration systems.
| Feature | Advantage | Limit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Elastomer Seal | Zero-leak performance | Temperature limits of rubber | |
| Flat Face | Unlimited reassembly | Requires flat alignment | |
| Vibration Damping | Prevents loosening | Higher initial cost |
Analysis: Switching to ORFS in high-vibration zones can reduce leak-related maintenance tickets by over 50%.
What Benefits Does a JIC Hydraulic Fitting Offer?

A JIC (Joint Industry Council) hydraulic fitting offers the benefit of a standardized, versatile connection that relies on a 37-degree metal-to-metal flare seating for a reliable seal. These fittings are incredibly popular because they are widely available, cost-effective, and compatible with a vast array of global equipment standards.
What is the 37-degree cone seat?
Here’s the breakdown: The male cone and female flare mate perfectly at a 37-degree angle to seal mechanically.
- Creates a large sealing surface area.
- Resists blowout under high pressure.
- Eliminates the need for thread sealant.
Is JIC compatible with most hose types?
You will notice JIC fittings on everything from tractors to manufacturing robots.
- Adapts to inch and metric tubing.
- Fits standard SAE hose ends.
- Interchangeable between brands easily.
How easy is it to assemble and reassemble?
JIC fittings are a favorite among field mechanics for their simplicity.
- Requires only two wrenches to tighten.
- Can be disconnected and reconnected multiple times.
- Visual inspection confirms proper seating.
Key Takeaway
JIC provides a universal, easy-to-service solution for most hydraulic needs.
| Benefit | Description | Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Versatility | Universal standard | High availability | |
| Serviceability | Simple tools needed | Low downtime | |
| Reliability | Metal-to-metal seal | Proven track record |
Analysis: JIC fittings are the best inventory staple for mixed fleets due to their broad compatibility.
Where Is a Metric DIN Hydraulic Fitting Most Common?

Metric DIN hydraulic fittings are most common in European-manufactured heavy equipment and machinery, adhering to the rigorous German Institute for Standardization (DIN) specifications. These fittings are essential for maintaining the integrity of imported excavators, loaders, and industrial presses that utilize metric tubing sizes.
How does it meet global ISO standards?
It’s important to note that DIN standards often align directly with ISO requirements for international consistency.
- Ensures safety across borders.
- Guarantees material quality and tolerance.
- Standardizes pressure ratings globally.
Is it best for metric-sized tubing?
Here’s the kicker: You simply cannot safely force an inch-sized fitting onto a metric tube.
- Provides exact tolerance match.
- Prevents tube deformation or crimping issues.
- Ensures full pressure retention.
Does it provide a secure, heavy-duty seal?
DIN fittings often feature a “bite type” ring that grips the tube securely.
- Withstands massive pressure surges.
- Resists pull-out forces on the tube.
- Maintains seal under thermal expansion.
Key Takeaway
DIN fittings are non-negotiable for maintaining European heavy machinery.
| Spec | Standard | Application | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thread | Metric | European Equipment | |
| Sealing | Bite type / O-ring | High Pressure | |
| Standard | DIN / ISO | Global Construction |
Analysis: Never attempt to cross-thread DIN with SAE fittings; standardizing on the correct metric parts prevents catastrophic port damage.
How Do Compression Hydraulic Fittings Connect Tubing?

Compression hydraulic fittings connect tubing by compressing a ferrule or “olive” against the tube wall as the nut is tightened, creating a grip that seals the fluid path. This method is distinct because it requires no flaring, soldering, or welding, making it a quick and effective solution for rigid tubing assembly.
Do they work well on thin-walled pipes?
You might be surprised that compression fittings are actually safer for thinner walls than flare fittings.
- Distributes load without splitting the tube.
- Prevents wall thinning during installation.
- Supports the tube structure internally.
Is installation possible without flaring?
This is the primary advantage of the compression style.
- No flaring tools required.
- Reduces installation time significantly.
- Allows for assembly in tight spaces.
What are the risks of improper installation?
Watch out for this: Over-tightening is the enemy of a compression seal.
- Crushes the ferrule too much, causing leaks.
- Can deform the tube permanently.
- Undermines the structural grip.
Key Takeaway
Compression fittings offer fast, tool-free assembly for rigid lines.
| Step | Action | Consequence of Error | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Insert | Slide nut/ferrule on | Leak if omitted | |
| Seat | Bottom out the tube | Gap creates void | |
| Tighten | Turn nut to spec | Crush/Leak if forced |
Analysis: Use compression fittings for hard-to-reach rigid lines where using a flaring tool is physically impossible.
How Do I Choose the Correct Hydraulic Fitting?
Choosing the correct hydraulic fitting requires a systematic evaluation of the STAMP method: Size, Temperature, Application, Media, and Pressure. Neglecting just one of these variables can lead to a mismatch that compromises the safety and efficiency of your entire hydraulic operation.
Does the system pressure impact choice?
Absolutely. High-pressure systems disqualify certain materials and designs immediately.
- NPT threads may weep at high pressure.
- Brass may shear under extreme surges.
- Steel JIC or ORFS handles 5000+ PSI.
How do I check for fluid compatibility?
Don’t ignore this: The fluid inside must not eat the seal or metal.
- Petroleum oils need standard Buna-N seals.
- Phosphate esters require Viton seals.
- Acids require stainless steel bodies.
Why does vibration affect fitting selection?
System movement will loosen simple thread connections over time.
- Vibration backs off NPT nuts.
- ORFS resists shaking loose best.
- Soft seal fittings absorb the energy.
Key Takeaway
Evaluate Pressure, Media, and Vibration before purchasing.
| Criteria | Low Pressure (<1000 PSI) | High Pressure (>3000 PSI) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vibration | Brass / NPT | ORFS / DIN | |
| Static | Iron / Compression | JIC / Flange | |
| Media | Water / Air | Hydraulic Oil |
Analysis: Prioritizing pressure rating and vibration resistance over initial cost prevents catastrophic field failures.
What Are the Steps to Install a Hydraulic Fitting?
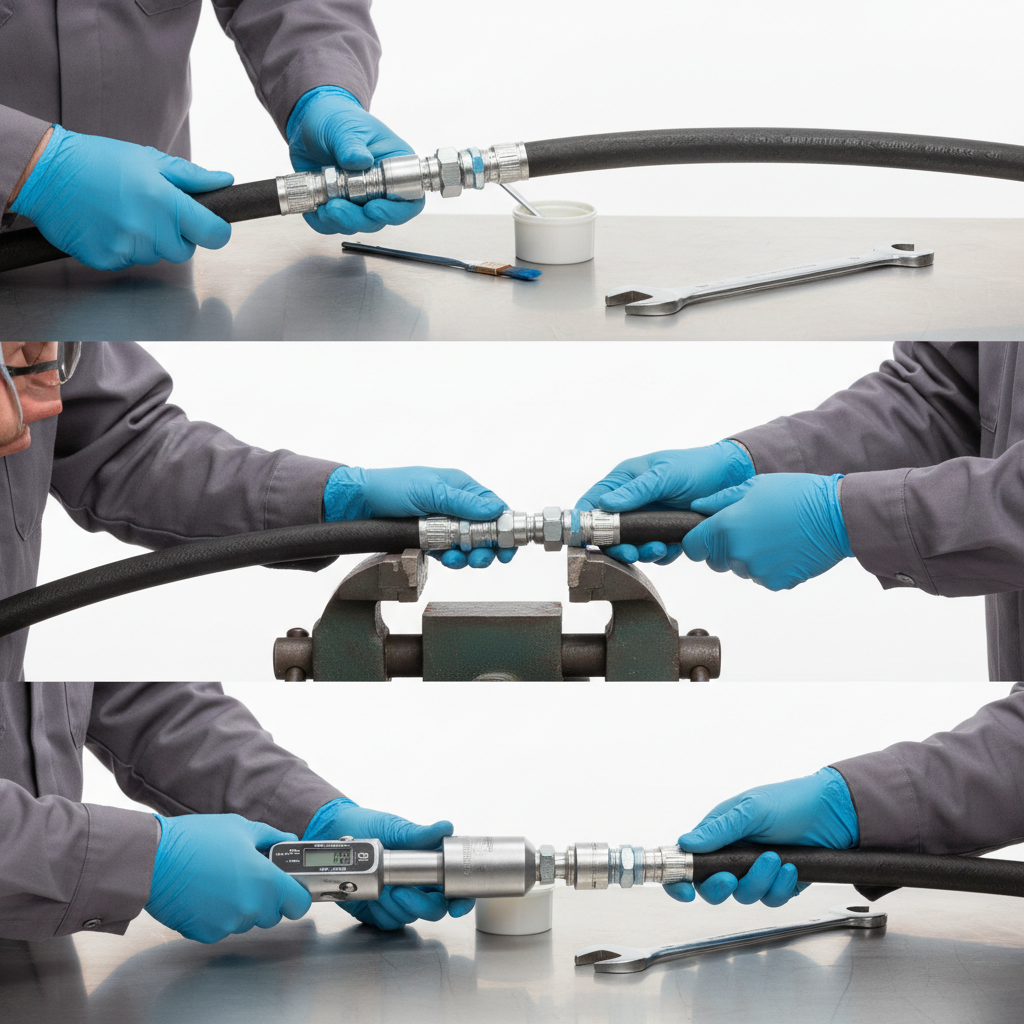

Installing a hydraulic fitting correctly follows a strict protocol of cleaning, aligning, and torquing to specification to ensure a safe and long-lasting seal. Rushing this process or guessing torque values is the leading cause of “mysterious” leaks that appear shortly after maintenance. For detailed guides, you can always explore our technical insights .
Do I need specialized tools for assembly?
Here’s the deal: While basic wrenches work, torque wrenches are critical for success.
- Ensures exact clamping force.
- Prevents thread stripping.
- Avoids under-tightening leaks.
How do I prevent over-tightening?
Over-tightening is a common rookie mistake that ruins fittings.
- Use the “flats from wrench resistance” method.
- Follow manufacturer torque charts strictly.
- Mark the nut position after tightening.
Why is cleaning the connection vital?
Dirt is the kryptonite of hydraulic systems.
- Grit prevents a flush face seal.
- Contaminants damage pump internals.
- Debris can cut O-rings during assembly.
Key Takeaway
Cleanliness and correct torque are the pillars of installation.
| Step | Tool Needed | Objective | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Solvent/Cloth | Remove grit | |
| Align | Hands | Prevent cross-thread | |
| Torque | Torque Wrench | Secure seal |
Analysis: Implementing a “Torque and Mark” protocol visually guarantees that every fitting has been properly tightened.
How Can You Prevent Hydraulic Fitting Leaks?
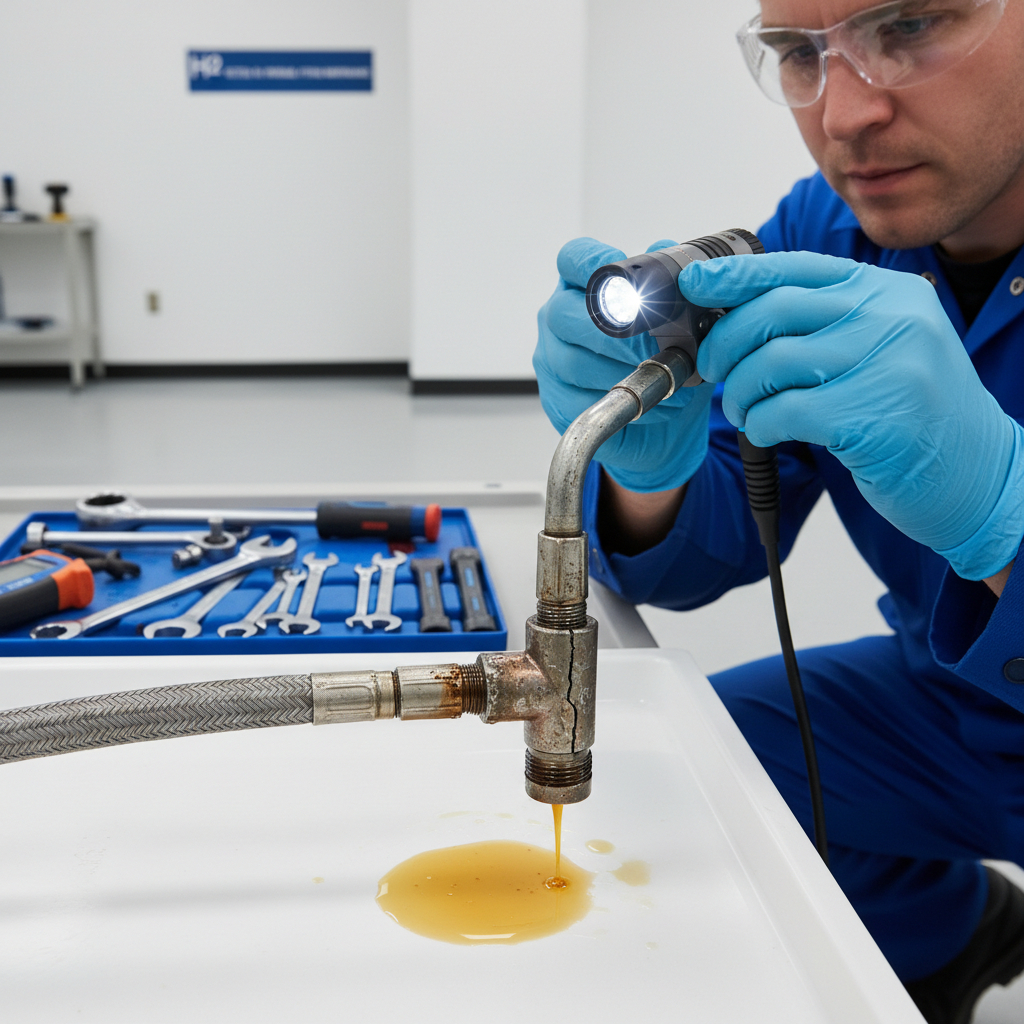

Preventing hydraulic fitting leaks starts with a proactive maintenance schedule and ends with using components from a manufacturer with rigorous quality control. Leaks are rarely sudden accidents; they are usually the result of ignored warning signs or sub-par parts entering the supply chain. Trusting a supplier with an ISO 9001 certified manufacturing process ensures the parts you install are defect-free.
What are the signs of a failing seal?
Keep an eye out for these early indicators before a blowout occurs.
- Wetness or oil sheen on the fitting.
- Pooling fluid on the floor below.
- Drop in system pressure readings.
How often should fittings be inspected?
Regular intervals catch problems while they are small.
- Daily visual checks for operators.
- Monthly torque checks for maintenance.
- Annual replacement of O-rings.
Why is high-quality manufacturing important?
Cheap fittings often have poor thread engagement.
- Inconsistent tolerances cause leaks.
- Weak materials crack under pressure.
- Poor plating leads to rust seizing.
Key Takeaway
Proactive inspection and quality parts eliminate 90% of leaks.
| Action | Frequency | Goal | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visual Check | Daily | Spot early drips | |
| Tighten | Monthly | Correct loosening | |
| Replace | Annually | Renew elastomers |
Analysis: A zero-leak policy is achievable only when high-quality parts are paired with a disciplined inspection schedule.
Conclusion
From durable stainless steel options to versatile JIC types, the right hydraulic fitting is the backbone of any fluid power system. Ignoring the specific needs of pressure, vibration, and environment will only lead to downtime and danger. Ensure you are using the precise fitting for your specific pressure and environmental needs to maximize equipment productivity. For expert guidance and premium components, contact us today .
FAQ
Q1: Can I mix different brands of hydraulic fittings?While it is technically possible if they adhere to the same standard (like SAE or ISO), it is generally best to stick to one manufacturer. Slight variations in tolerance or material quality between brands can compromise the seal integrity at high pressures, leading to unexpected leaks.
Q2: How do I know if a hydraulic fitting is reusable?You should judge reusability based on the fitting type and condition. O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) fittings are designed to be reused by simply replacing the O-ring, whereas compression or flare fittings that rely on metal deformation should often be replaced after disassembly to ensure a safe seal.
Q3: What is the best hydraulic fitting for high pressure?The O-Ring Face Seal (ORFS) and DIN heavy-series fittings are typically the best choices for high-pressure applications. Their design eliminates the risk of flaring out or weeping fluid, which is common with tapered thread fittings under extreme stress.
Q4: How do I measure a hydraulic fitting thread?You need to use a caliper to measure the outer diameter (for male) or inner diameter (for female) and a thread pitch gauge to determine the distance between threads. Comparing these two precise measurements against a standard thread identification chart is the only way to accurately identify the fitting type.
Q5: Can I use a brass fitting for high-temperature oil?You should be very cautious, as standard brass may lose strength at high temperatures. While brass handles heat relatively well, the specific alloy and the pressure of the hot oil system must be considered; for high-temp, high-pressure oil, stainless steel is usually the safer and more reliable option.